Almost two in five disadvantaged pupils were “persistently” absent from school last academic year, more than double the rate among non-disadvantaged pupils, new government data shows.
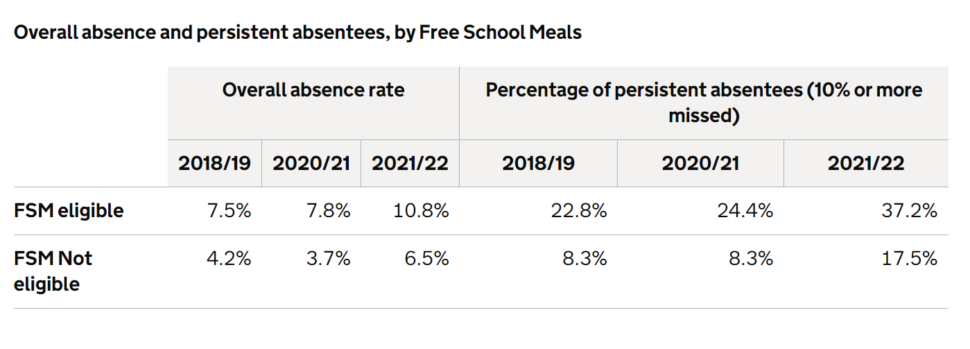
Pupil absence statistics for 2021-22 shows 37.2 per cent of pupils eligible for free school meals missed 10 per cent or more sessions, compared to 17.5 per cent of their better-off peers.
In the previous year, 24,4 per cent of disadvantaged pupils and 8.3 per cent of non-disadvantaged pupils were persistently absent.
It comes after MPs were warned last week of “serious” levels of persistent absence among pupils. The government has made tackling the issue a priority.
Absence soared for all pupils in the aftermath of Covid lockdowns.
Overall absence rose from 4.6 per cent in 2020-21 to 7.6 per cent last year, and persistent absence increased from 12.1 per cent to 22.5 per cent over the same period, equating to around 1.6 million pupils.
Severe absence – the proportion of pupils missing 50 per cent or more sessions – also rose from 1.1 per cent in 2020-21 to 1.7 per cent last year, equating to around 120,000 pupils.
Some groups of pupils were far more likely to be persistently absent last year than others.
Pupils with SEND more likely to be absent
Persistent absence among pupils with a statement of special educational needs and disabilities was 36.9 per cent last year, down slightly from 42.3 per cent in 2020-21 but up significantly on pre-pandemic 2018-19, when the rate was 24.6 per cent.
Thirty-two per cent of pupils receiving SEN support were persistently absent last year, up from 18.9 per cent the year before and 17.9 per cent in 2018-19.
Older pupils were also much more likely to be persistently absent last year, with rates of 36 per cent among sixth formers and 32.2 per cent among year 11s, compared with 16.6 per cent among year 3s.
Persistent absence was highest among pupils of Irish Traveller heritage (71.7 per cent) and Gypsy and Roma pupils (64.9 per cent), and lowest among Chinese (6.2 per cent) and Black African pupils (10.4 per cent).
Pupils were more likely to be persistently absent in the north east (24.7 per cent), Yorkshire and the Humber (24 per cent) and West Midlands (24 per cent) and least likely in outer London (19.6 per cent) and inner London (19.7 per cent).
There was little divergence by gender, however, with 22.8 per cent of girls and 22.2 per cent of boys persistently absent last year.
Illness driving rise in absences
A rise in the overall absence rate last year was driven mostly by an increase in illness absence, which rose from 2.1 per cent in 2020-21 to 4.4 per cent in 2021-22. This includes positive Covid cases but not those at home for other Covid-related reasons.
But the DfE also reported an increase in unauthorised absence, from 1.3 per cent in 2020-21 to 2.1 per cent in 2021-22.
Last week, witnesses at a hearing of the Parliamentary education committee warned better-off parents were abusing the system of fines for term-time holidays.
However, the rate of unauthorised holidays reported by the DfE stood at 0.4 per cent last year, the same rate as between 2016 and 2020.
MPs were also told schools were misusing attendance codes to avoid being “caught out” doing “managed moves”.
Dame Rachel de Souza, the children’s commissioner for England, said Ofsted should hold councils to account for falling attendance to ensure a “razor-sharp focus” on the issue.









Your thoughts